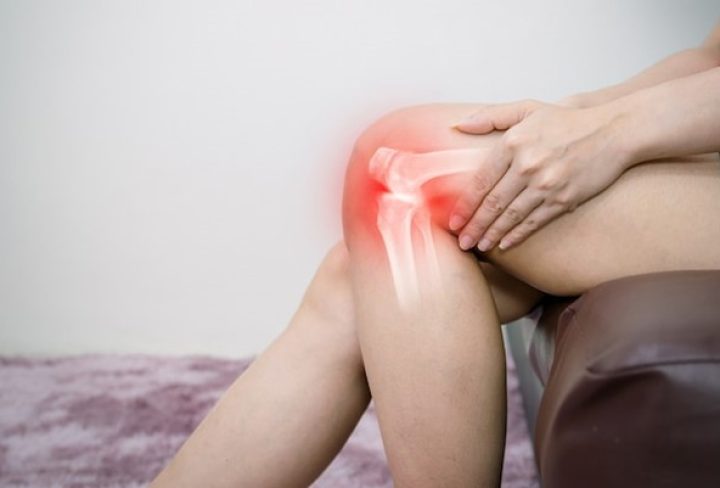
Tendonitis, also known as tendinitis, is a common condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of a tendon, the thick cord that attaches muscle to bone.
Causes of Tendonitis
Tendonitis can be caused by various factors, including:
- Overuse or repetitive movements: Activities that involve repetitive motion or overuse of a particular tendon, such as typing, gardening, or playing sports, can lead to tendonitis.
- Aging: Tendons become less flexible and more prone to injury with age, increasing the risk of tendonitis.
- Poor posture or biomechanics: Incorrect posture or biomechanics during physical activities can put excessive stress on tendons, leading to inflammation and injury.
Symptoms of Tendonitis
Common symptoms of tendonitis may include:
- Pain, tenderness, or swelling near a joint or tendon
- Stiffness or reduced range of motion in the affected area
- Weakness or difficulty performing activities that involve the affected tendon
- Crepitus or crackling sensation when moving the affected joint
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tendonitis
Diagnosis of tendonitis typically involves a physical examination by a docotr and may include imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI to assess the extent of tendon damage. Treatment options for tendonitis may include:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms and giving the affected tendon time to heal.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to the affected area to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Specific exercises and stretches to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and promote healing of the affected tendon.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroid injections to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Orthotic devices: Braces, splints, or supports to provide stability and reduce stress on the affected tendon.
Prevention of Tendonitis
To reduce the risk of tendonitis, it’s important to:
- Warm up properly before physical activity and cool down afterward to prevent muscle fatigue and injury.
- Use proper technique and equipment during physical activities to avoid putting excessive stress on tendons.
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of physical activities to allow tendons to adapt and strengthen over time.
- Take regular breaks and vary activities to avoid overuse of specific tendons.
While tendonitis can be painful and debilitating, with proper treatment and prevention strategies, most individuals can recover fully and return to their normal activities.
Are you experiencing symptoms of tendonitis? Consult with doctor for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.